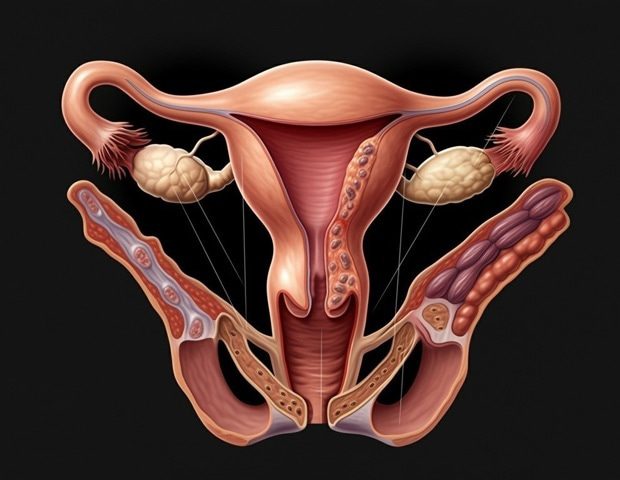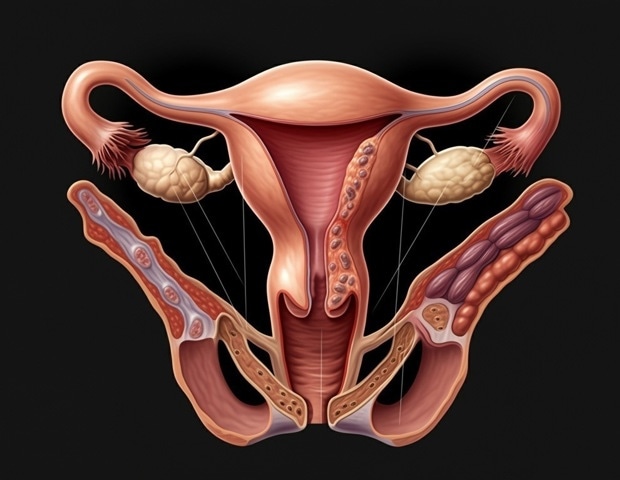
Almost 200 million people, including children, around the world have endometriosis, a chronic disease in which the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus. More severe symptoms, such as extreme pain and potentially infertility, can often be mitigated with early identification and treatment, but no single point-of-care diagnostic test for the disease exists despite the ease of access to the tissue directly implicated. While Penn State Professor Dipanjan Pan said that the blood and tissue shed from the uterus each month is often overlooked – and even stigmatized by some – as medical waste, menstrual effluent could enable earlier, more accessible detection of biological markers to help diagnose this disease.
Pan and his group…
Disclaimer
We strive to uphold the highest ethical standards in all of our reporting and coverage. We 5guruayurveda.com want to be transparent with our readers about any potential conflicts of interest that may arise in our work. It’s possible that some of the investors we feature may have connections to other businesses, including competitors or companies we write about. However, we want to assure our readers that this will not have any impact on the integrity or impartiality of our reporting. We are committed to delivering accurate, unbiased news and information to our audience, and we will continue to uphold our ethics and principles in all of our work. Thank you for your trust and support.
Website Upgradation is going on. For any glitch kindly connect at 5guruayurveda.com